This is the first post in a series for building your very own Fitbit app. It will cover some of the most useful features of the SDK including geolocation, remote connectivity, transferring information between your phone and watch, and the user interface of the application itself.

In this tutorial I will cover project setup and a little bit about the “companion” application. Now, head over to Fitbit Studio and let’s get coding!
- Create a new “Starter” project.

- If you haven’t already, install the Fitbit OS Simulator. Run the project with the simulator selected.

- Open the companion JavaScript file. This file runs code on your phone or computer when the App is launched. We will use it to query a weather API and send the forecast to the watch.

We need to get the current location of the watch (or companion device), so that we can use it in our query to the weather service. For convenience, we will obtain the geolocation with the companion app since we are also making the query to the weather service here.
The geolocation event handler is used to obtain the current location. It requires the functions locationSuccess() and locationError().
import { geolocation } from "geolocation";
geolocation.getCurrentPosition(locationSuccess, locationError, {
timeout: 60 * 1000
});- locationError() can be used to log a meaningful message to the console when GPS isn’t behaving as expected.
function locationError(error) {
console.log("Error: " + error.code, "Message: " + error.message);
}- The current location is stored in a variable. This will be necessary to get a weather forecast for the user.
var current_location;
function locationSuccess(position) {
current_location = position.coords.latitude + "," + position.coords.longitude
console.log("Current location: " + current_location);
}- Run the project, you will see the coordinates for the Simulator in the console. You can try this on your watch as well!
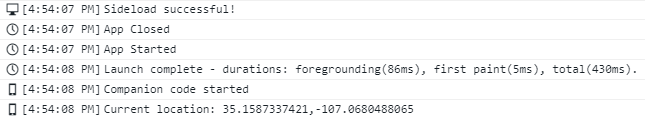
In Part 2, we will send these coordinates to the weather service to get a forecast. The full project is available on GitHub, delineated into four parts. Stay tuned and happy coding!
Leave a comment